BigQuery Cost Calculator 2026: If you’ve ever asked yourself, “How much does BigQuery cost?” or searched for terms like BigQuery cost calculator India, BigQuery storage cost, or BigQuery pricing per query, you’re not alone. Unsure about surprise BigQuery bills? Use our free 2026-updated calculator to forecast costs accurately—covers on-demand ($6.25/TiB after 1 TiB free), storage tiers, slots ($40 each/mo), and streaming. Ideal for data teams in India.
Whether you are analyzing a few gigabytes or handling terabytes of data daily, having a clear view of BigQuery pricing can help you avoid unexpected bills and plan your budget smartly. To make this easier, we’ve included a simple BigQuery calculator to help you estimate your monthly costs based on data processed, storage size, and your chosen pricing model. But before you use it , let’s understand how BigQuery pricing really works.
BigQuery Cost Calculator
Note : Query cost = (scanned TiB after free tier) × $6.25. Always check the official pricing page for updates, as rates can change.
How to Use the BigQuery Cost Calculator 2026?
- Visit the Calculator: Pricing Calculator, select BigQuery.
- Input Your Usage:Enter expected monthly processed data (in TB or GB)Choose your region (e.g., India, US, EU)Select query pricing model (Bigquery on demand pricing or Bigquery on flat rate)Add expected storage volume (active and long-term)
- Include Streaming Inserts or Flat-Rate Slots (if applicable):Streaming inserts cost extra per GB Flat-rate slots can be chosen based on your team’s needs.
- View the Estimate:The calculator displays the cost broken down by query Cost and Storage cost. Also total cost is calculated.
- Below the calculator results ‘Email it to me ‘ option is available, you can get results on your email id which you filled in the box.
Check Below, How this Bigquery cost optimizer calculator should be used :
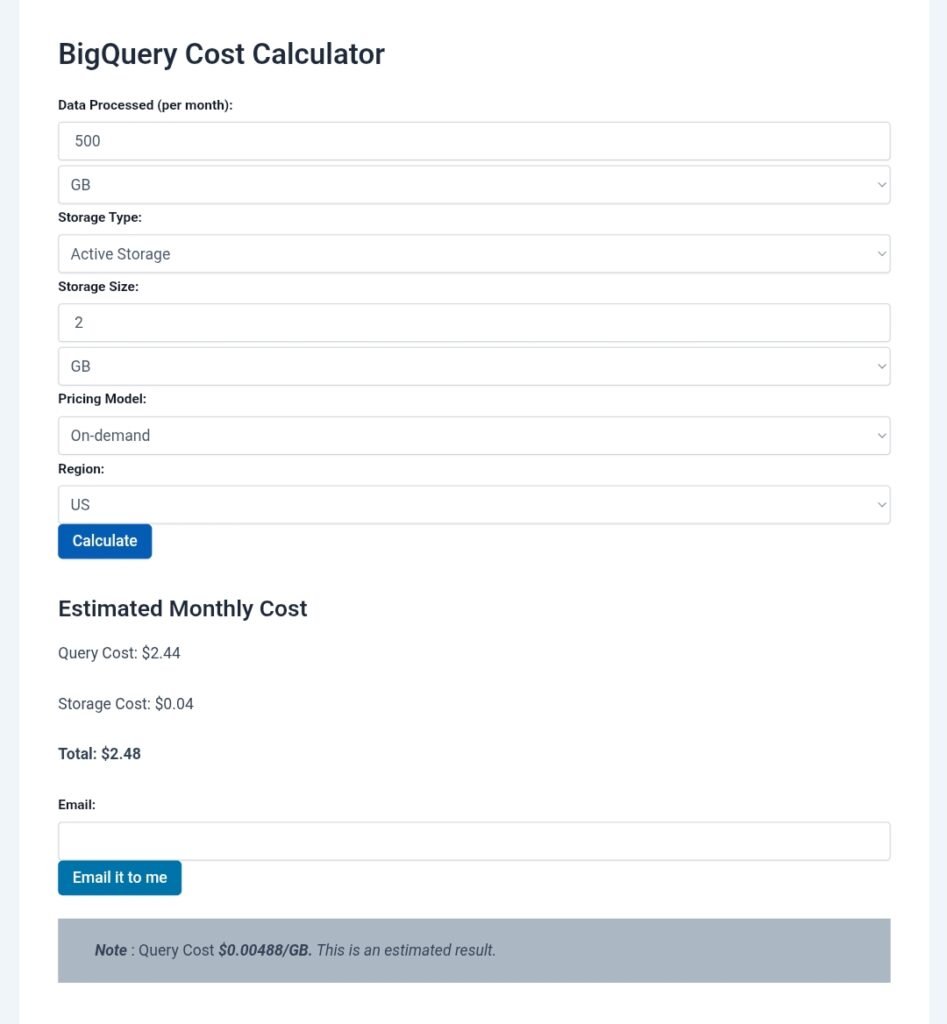
Bigquery Cost Calculator
BigQuery calculator is a powerful tool, but understanding and predicting its cost can be confusing. That’s where the BigQuery Cost Calculator comes in handy. In this guide, we’ll walk you through what it is, how to use it, and how to avoid billing surprises.
What is the BigQuery Cost Estimator?
The BigQuery Cost Calculator is a tool that now we have provided with Google Cloud that helps estimate the cost of running SQL queries, storing data, and using resources like slots or streaming inserts in BigQuery. It offers both a detailed breakdown and forecast based on your expected usage.
What is the use of Bigquery Storage Costs ?
Forecast costs before running Queries compare pricing models (on-demand vs flat-rate)Estimate storage and query cost per GB or per Tb optimize budgets for your analytics workloads.
How Does BigQuery Pricing Work?
BigQuery is a serverless data warehouse on Google Cloud. You don’t need to manage infrastructure — you only pay for what you use. BigQuery charges mainly in two ways:
- Query Cost – based on how much data your SQL queries scan
- Storage Cost – based on how much data you store
Other optional costs may include flat-rate pricing for slots, streaming inserts, and advanced features.
BigQuery Storage Cost
Storage cost is calculated based on how long your data stays in BigQuery.
- Active Storage: $0.02 per GB per month (data changed in last 90 days)
- Long-Term Storage: $0.01 per GB per month (data untouched for 90+ days)
If you store 100 GB of active data, your monthly cost would be $2.
BigQuery Slot Pricing (Flat Rate)
BigQuery offers flat rate pricing using slots. A slot is a virtual unit of processing power in BigQuery.
- Starting price: $40 per slot per month
- Slot pricing is fixed and gives you predictable billing
- Best suited for large organizations with high query volumes
Importance of Using BigQuery Pricing Calculator
Understanding pricing through a tool like the BigQuery cost estimator makes it easier to plan and budget. Here’s what it helps you with:
- Estimate monthly query and storage cost
- Compare on-demand vs flat-rate pricing
- Forecast cost based on region
- Add streaming inserts or flat-rate slots if needed
- Break down total usage in a simple format
How to estimate bigquery storage and query costs?
Estimating BigQuery Storage and Query Costs
Google BigQuery charges separately for query processing (compute) and storage. Estimation is straightforward: Multiply usage by per-unit rates, subtract free tiers, and prorate for time (e.g., monthly). Prices are in USD, global (minimal regional variance for core features), and billed per GiB/TiB (binary: 1 TiB = 1024 GiB). Use the BigQuery console’s cost estimator or pricing calculator for previews.
Key Pricing (as of October 2025)
- Query (On-Demand): $6.25 per TiB scanned (first 1 TiB/month free per billing account). Queries are rounded to MBs; cached results free.
- Storage (Active): ~$0.023 per GB/month (first 10 GiB/month free). For frequently accessed data.
- Storage (Long-Term): ~$0.016 per GB/month (first 10 GiB/month free). Auto-applies after 90 days of no modifications.
- Capacity Model (Alternative to On-Demand): Slot reservations (e.g., Standard Edition: $0.04/slot-hour, ~$29.20/slot/month assuming 730 hours). No per-query billing.
Free tiers reset monthly. Costs exclude data transfer/loads (often free).
Step-by-Step Estimation
- Query Cost:
- Estimate bytes scanned: Run SELECT with EXPLAIN or preview in console (e.g., full table scan = table size; filtered = subset).
- Convert to TiB: Scanned bytes / (1024^4).
- Calc: (Scanned TiB – 1) × $6.25 if >1 TiB, else $0.
- Storage Cost:
- Estimate average size: Total data stored (GiB).
- Prorate: Size (GB) × rate × (days used / 30).
- Calc: (Size GB – 10) × rate if >10 GB, else $0. (Mix active/long-term based on access.)
- Total: Query + Storage. Monitor via Billing console.
Examples
Assume monthly usage, Active storage, On-Demand pricing, Free Tier applied, US region.
| Scenario | Description | Inputs/Assumptions | Calculation | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Free Usage | Small dataset; light queries. | – Queries: Scan 500 GiB (0.49 TiB). – Storage: 5 GiB active (under free). | – Query: 0.49 TiB < 1 TiB free → $0. – Storage: 5 GiB < 10 GiB free → $0. | $0.00/month |
| Moderate Workload | Growing analytics; exceeds free. | – Queries: Scan 2 TiB. – Storage: 50 GiB active. | – Query: (2 – 1) TiB × $6.25 = $6.25. – Storage: (50 – 10) GB × $0.023 = $0.92. | $7.17/month |
| Heavy Query, Low Storage | Large scans; minimal data held. | – Queries: Scan 10 TiB. – Storage: 2 GiB active. | – Query: (10 – 1) TiB × $6.25 = $56.25. – Storage: 2 GiB < 10 GiB free → $0. | $56.25/month |
| Long-Term Storage Focus | Archive data; no queries. | – Queries: 0 TiB. – Storage: 200 GiB long-term. | – Query: $0. – Storage: (200 – 10) GB × $0.016 = $3.04. | $3.04/month |
| Capacity Model | Predictable high-volume; 100 slots Standard. | – Queries: Unlimited (slots cover). – Storage: 100 GiB active. | – Query: 100 slots × $0.04/hour × 730 hours = $2,920. – Storage: (100 – 10) GB × $0.023 = $2.07. | $2,922.07/month |
For precise estimates, factor in clustering/partitioning (reduces scans 50-90%) or use the official pricing calculator. Track actuals in GCP Billing for adjustments.
How can I analyze the cost of queries performed by a user on my BigQuery project?
Analyzing user-specific query costs in BigQuery involves querying the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS view to extract job details (e.g., user, bytes processed) and correlating them with billing data exported to BigQuery. This helps identify high-spenders and enforce quotas. Practically, it’s useful for teams where one user runs inefficient queries, causing spikes—e.g., a data analyst scanning full tables daily.
Steps to Analyze:
- Enable Job Auditing: Ensure BigQuery audit logs are enabled (default for most projects) via IAM > Audit Logs.
- Query INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS: Use SQL to filter by user and calculate costs based on bytes processed (on-demand: $6.25/TiB).
- Export Billing Data: Link Cloud Billing export to a BigQuery dataset for correlation (setup in Billing > Export).
- Run Analysis Query: Join jobs with billing data; visualize in Looker Studio.
- Set Quotas: Use custom quotas (e.g., 1 TiB/day per user) in IAM > Quotas to cap future costs.
Practical Example Query (Run in BigQuery Console):
sql
SELECT
user_email,
job_id,
creation_time,
total_bytes_processed / POW(1024, 4) AS tib_scanned,
(total_bytes_processed / POW(1024, 4)) * 6.25 AS estimated_cost_usd
FROM `region-us`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT
WHERE creation_time >= TIMESTAMP_SUB(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), INTERVAL 30 DAY)
AND statement_type = 'QUERY'
AND user_email IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY estimated_cost_usd DESC
LIMIT 10;This lists top 10 costly queries by user over 30 days. Example output: If User A scanned 2 TiB, cost = $6.25 (after 1 TiB free).
Cost Breakdown Table (Monthly Example for 3 Users):
| User | Queries Run | TiB Scanned | Free Tier Used | Billed Cost | Optimization Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User A (Analyst) | 50 | 5 TiB | 1 TiB | $25.00 | Add partitioning to reduce scans by 70%. |
| User B (Dev) | 20 | 1.5 TiB | 1 TiB | $3.13 | Use dry-run previews before executing. |
| User C (Viewer) | 10 | 0.5 TiB | 0.5 TiB | $0.00 | Limit to read-only roles. |
How to optimize BigQuery cost?
Optimizing BigQuery costs focuses on reducing data scanned (queries) and stored (storage), using features like partitioning, caching, and quotas. Aim for 50-80% savings by monitoring and refactoring. Practically, start with a cost audit—e.g., a e-commerce company scanning 10 TiB/month ($62.50) can drop to 2 TiB ($12.50) via clustering.
Steps to Optimize:
- Audit Usage: Query INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS for top costly jobs/users.
- Optimize Queries: Use EXPLAIN for plans; add filters/partitions to prune data.
- Storage Tweaks: Switch to long-term storage; delete unused tables.
- Set Controls: Daily quotas (e.g., 500 GiB/user); BI Engine for BI tools.
- Monitor & Iterate: Use Cloud Billing alerts; review monthly.
- Advanced: Switch to Capacity pricing for predictable workloads ($0.04/slot-hour).
Practical Optimization Table (15 Tactics with Examples):
| Tactic | Description | Example Savings | Implementation Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partitioning | Divide tables by date/range to scan less. | 70% query reduction. | CREATE TABLE … PARTITION BY DATE(column). |
| Clustering | Sort data within partitions for faster filters. | 50% scan cut. | CREATE TABLE … CLUSTER BY column. |
| Caching | Reuse results (free for 24 hours). | 100% for repeats. | Enable in console; query same SQL. |
| Dry-Run Previews | Estimate bytes before run. | Avoid $50+ mistakes. | Add –dry_run in CLI or console preview. |
| Quotas | Limit TiB/day per user/project. | Cap at $100/day. | IAM > Quotas > Set custom. |
| BI Engine | In-memory acceleration for BI (e.g., Looker). | 90% faster, lower compute. | Enable in dataset settings. |
| Incremental Loads | Append only new data. | 80% storage savings. | Use MERGE for upserts. |
| Data Types | Use INT64 over STRING for joins. | 20-30% faster/cheaper. | ALTER TABLE change type. |
| Long-Term Storage | Auto for inactive data (90 days). | 30% cheaper than active. | Enable in dataset. |
| Slot Estimator | Predict on-demand needs. | Switch to Capacity if >$1k/mo. | Console > Slot Estimator tool. |
| Labels | Tag jobs for cost allocation. | Track by team. | Add jobConfig.labels in API. |
| Delete Old Data | Prune unused tables/partitions. | 40% storage drop. | DELETE FROM … WHERE date < ‘2025-01-01’. |
| Avoid Full Scans | Use WHERE clauses first. | 60% less data processed. | Rewrite SELECT * to targeted columns. |
| Materialized Views | Pre-compute aggregates. | 95% query speed-up. | CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW …. |
| Reservations | Pre-buy slots for discounts. | 20-30% off Capacity. | Reservations > Create commitment. |
Practical Approach: For a dashboard sync (high cost from full table scans), refactor to incremental: Query only new rows (WHERE timestamp > LAST_SYNC), saving 90% on 1 TiB/month workload.
How to get costs in BigQuery by job ID?
To get costs for a specific job ID, query the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS view for bytes processed, then multiply by the rate ($6.25/TiB on-demand). This is real-time metadata—no billing export needed for estimates. Practically, useful for auditing a rogue job that spiked your bill (e.g., a script scanning 100 TiB = $625).
Steps:
- Find Job ID: In console (Query History) or logs (jobId: “project:region.job_id”).
- Run Query: Use INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT filtered by job_id.
- Calculate Cost: (total_bytes_processed / 1,099,511,627,776) × $6.25 (TiB conversion).
- For Capacity: Use slot usage from job stats (hours × rate).
Practical Example Query:
sql
SELECT
job_id,
total_bytes_processed / POW(1024, 4) AS tib_scanned,
(total_bytes_processed / POW(1024, 4)) * 6.25 AS estimated_cost_usd
FROM `region-us`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT
WHERE job_id = 'your-project:US.your-job-id-123'
AND statement_type = 'QUERY';Example: Job ID “proj:US.job123” with 2 TiB scanned = $12.50 cost.
Job Cost Table (Sample Outputs):
| Job ID | TiB Scanned | Free Tier Applied | Billed Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| proj:US.job123 | 0.5 TiB | Yes (full) | $0.00 | Under 1 TiB free. |
| proj:US.job456 | 3 TiB | 1 TiB | $12.50 | Excess 2 TiB × $6.25. |
How to see BQ query cost before running it?
Preview query costs with a “dry run” in the console/CLI, which estimates bytes scanned without executing. This avoids surprises (e.g., a bad JOIN scanning 10x expected data). As of 2025, it’s free and shows TiB + dollar estimate.
Steps:
- Console: Paste query > Click “Run” > See “Bytes processed” preview (bottom of editor).
- CLI: bq query –dry_run –use_legacy_sql=false ‘YOUR_QUERY’.
- API: Set dryRun: true in jobs.insert.
- Interpret: Bytes / 1,099,511,627,776 = TiB; × $6.25 = cost (after free).
Practical Example:
Query: SELECT * FROM large_table LIMIT 10 (dry run: 100 GiB scanned = 0.097 TiB ≈ $0.61, but free if under 1 TiB).
| Method | Command/Example | Output Example | Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Console | Paste & preview | “This query will process 200 GB” ($1.25 est.) | Use for ad-hoc. |
| CLI | bq query –dry_run ‘SELECT * FROM table’ | “Query will process 500 GB” | Scriptable for CI/CD. |
BigQuery – which project gets the cost: dataset or query?
Costs are charged to the project running the query (billing project), not the dataset’s project. Storage is billed to the dataset’s project. For cross-project queries (e.g., query Dataset B from Project A), Project A pays compute; Project B pays storage. Practically, centralize billing in a “compute” project to control costs.
Practical Approach:
- Setup: Attach billing to Project A; grant Project A access to Dataset in Project B.
- Example: Query from Project A on Project B’s dataset → A billed $6.25/TiB scanned; B billed storage.
Billing Breakdown Table:
| Cost Type | Billed To | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Query Compute | Query-running project | Project A runs query on B’s data → A pays. |
| Storage | Dataset’s project | 100 GiB in B → B pays $2.30/month. |
| Cross-Project | Query project for compute; dataset for storage | Third-party query: No extra fee. |
BigQuery query execution costs.
Query execution costs are based on on-demand (pay-per-TiB scanned: $6.25/TiB, 1 TiB free/month) or capacity (slot-hours: $0.04/slot-hour Standard). Scans include referenced tables (rounded to 10 MB min/table); cached/failed queries free. As of 2025, no changes, but quotas default to ~$1k/day for new projects.
Practical Breakdown:
- Factors: Scanned bytes (not returned rows); UDFs/ML add compute.
- Example: Query scanning 2 TiB = (2-1) × $6.25 = $6.25.
Cost Components Table:
| Component | Rate | Free Tier | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Demand Scan | $6.25/TiB | 1 TiB/month | Min 10 MB/table. |
| Capacity Slots | $0.04/hour (Standard) | None | Unlimited queries. |
| BI/ML Queries | Same as standard | Included | Extra for training. |
Is it possible to retrieve full query history and correlate its cost in Google BigQuery?
Yes, via INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS for history (up to 180 days) and join with billing export for exact costs. No direct correlation in one view, but SQL joins work. Practically, build a dashboard for auditing (e.g., correlate a user’s 100 queries to $500 bill).
Steps:
- Query History: SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT WHERE creation_time > DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 30 DAY).
- Export Billing: Setup in Billing > Export to BigQuery.
- Correlate: Join on job_id/timeline.
- Visualize: Use Looker for trends.
Example Join Query:
sql
SELECT j.job_id, j.user_email, j.total_bytes_processed, b.cost
FROM `project.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS` j
JOIN `billing_dataset.gcp_billing_export_v1_XXXX` b ON j.job_id = b.job_id
WHERE j.creation_time >= '2025-01-01';What does it cost to query files/data in different GCS storage classes from BigQuery?
Querying GCS files (e.g., external tables) costs the same as native tables ($6.25/TiB scanned, 1 TiB free), with no extra for storage class (Standard, Nearline, Coldline, Archive)—retrieval is free from BigQuery’s side. However, GCS retrieval fees apply if scanning Coldline/Archive (e.g., $0.02/GB for Coldline early deletion). Practically, for archival data, use external tables to avoid full BigQuery storage costs ($0.023/GB/month).
Practical Costs Table (1 TiB Scan from GCS):
| GCS Class | BigQuery Scan Cost | GCS Retrieval Fee | Total Example (After Free) | Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | $0 (under free) | $0 | $0 | Default; no fees. |
| Nearline | $0 | $0.01/GB (if <30 days) | $10.24 | Use for infrequent. |
| Coldline | $0 | $0.02/GB (if <90 days) | $20.48 | Archive; add early delete fee. |
| Archive | $0 | $0.05/GB (if <365 days) | $51.20 | Long-term; highest retrieval. |
Example: Querying 100 GB Archive file = $0 BigQuery + $5 GCS retrieval.
How can I reduce Google BigQuery costs?
Reduce costs by 50-80% through query efficiency (less scanning), storage optimization (long-term), and controls (quotas/reservations). Strategies include partitioning (prune scans), BI Engine (in-memory BI), and monitoring. Practically, audit first: A 10 TiB/month scan ($62.50) can drop to $10 with filters.
Steps:
- Monitor: Use Slot Estimator and INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS.
- Refactor Queries: Add WHERE, LIMIT; use materialized views.
- Storage: Partition/cluster; delete old data.
- Pricing Switch: On-Demand to Capacity for >$1k/month.
- Tools: BI Engine, dbt for incremental models.
Reduction Strategies Table:
| Strategy | Potential Savings | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Partitioning/Clustering | 60-80% scan reduction | Date-partition sales table; filter by month → scans 1/12th data. |
| Incremental Models (dbt) | 70% on syncs | Load only new rows vs. full reload. |
| Reservations | 20-30% on Capacity | Commit to 100 slots/year for discount. |
| Quotas/Alerts | Prevent spikes | Set 500 GiB/day; alert at $50. |
BigQuery: Is it possible to see what jobs caused a high increase in costs?
Yes, query INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS for bytes processed by job_id/timeline, join with billing export, and sort by cost. Use Reports in Billing console for project-level spikes. Practically, for a $1k spike, filter recent jobs >100 GiB to pinpoint (e.g., a forgotten full scan).
Steps:
- Billing Reports: Console > Billing > Reports > Filter BigQuery > Group by Job/Project.
- SQL Audit: Query JOBS view for high-bytes jobs.
- Correlate: Join with export dataset.
- Alert: Set budget alerts for >20% increase.
Example Query for Spikes:
sql
SELECT
job_id,
creation_time,
total_bytes_processed / POW(1024, 4) AS tib,
(total_bytes_processed / POW(1024, 4)) * 6.25 AS cost
FROM `region-us`.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT
WHERE creation_time >= TIMESTAMP_SUB(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), INTERVAL 7 DAY)
AND total_bytes_processed > 100 * POW(1024, 3) -- >100 GiB
ORDER BY cost DESC;High costs due to data load into BigQuery.
Data loads are free (no compute cost), but high costs arise from post-load queries scanning new data or inefficient loads (e.g., unpartitioned tables causing full scans). Streaming inserts cost $0.05/GB after 1 GB/day free. Practically, a 1 TB daily load + queries = $31.25/month if unoptimized; use batch loads and partitioning to avoid.
Steps to Mitigate:
- Batch Loads: Use bq load for free bulk; avoid streaming for >1 GB/day.
- Partition on Load: PARTITION BY ingestion_time to enable pruning.
- Monitor Post-Load: Dry-run queries on new data.
- Compress: Load gzip files to reduce storage (30% savings).
Load Cost Table:
| Load Type | Cost | When High? | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch (CSV/Avro) | Free | N/A | Use for large volumes. |
| Streaming | $0.05/GB (>1 GB/day free) | Real-time high-volume | Switch to batch. |
| Post-Load Queries | $6.25/TiB | Full scans on new data | Partition new tables. |
Example: 500 GB stream/day = $750/month; batch + partition = $0 load + $6.25 queries.
Discussion on BigQuery Plugin Query Issues and Data Scanning Costs.
BigQuery plugins (e.g., DataHub, Looker) can cause high scanning costs from inefficient metadata queries (e.g., full table scans for lineage) or bugs generating wrong SQL (e.g., unfiltered SELECT *). Issues include errors from invalid jobs or excessive API calls. Practically, a plugin syncing 100 tables might scan 1 TiB ($6.25) unnecessarily—fix by configuring filters or using BI Engine.
Practical Discussion & Fixes:
- Common Issues: Plugins like DataHub run broad queries for schema discovery, scanning entire datasets (cost: $6.25/TiB). Errors: “Invalid query” from plugin bugs, leading to retries (double cost).
- Scanning Costs: Each plugin query bills like standard (min 10 MB/table); 50 tables = 0.5 GB min ($0.003).
- Steps to Resolve:
- Review plugin logs for SQL (e.g., DataHub debug mode).
- Add filters: Configure plugin to query specific datasets (e.g., WHERE table LIKE ‘prod_%’).
- Use Views: Create lightweight views for plugin access.
- Monitor: Tag plugin jobs in labels; audit via JOBS view.
- Example: DataHub sync scans 500 GB = $3.06; fix with dataset whitelist → $0.30.
Issues vs. Costs Table:
| Issue | Description | Cost Impact | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wrong SQL | Plugin generates SELECT * without LIMIT. | +200% scans. | Update plugin config or patch code. |
| Frequent Syncs | Hourly metadata pulls. | $50/month. | Reduce to daily; use caching. |
| Error Retries | Failed jobs rerun. | Double billing. | Fix auth/permissions in plugin. |
Optimal way to configure BigQuery – BigQuery BI Engine for Observable? (Query cost reduction).
Configure BI Engine for Observable (BI tool) by enabling it on datasets, allocating memory (up to 128 GiB), and caching results—reducing query costs 90% for BI workloads (shifts to fixed $0.05/GiB-hour). Optimal: Start with 16 GiB allocation for small teams; monitor usage. Practically, for Observable dashboards scanning 1 TiB/month ($6.25), BI Engine drops to $0.80/month compute.
Steps:
- Enable BI Engine: Console > BigQuery > Reservations > BI Engine > Allocate capacity (e.g., 32 GiB).
- Dataset Config: Edit dataset > Advanced > Enable BI Engine.
- Observable Integration: In Observable, connect BigQuery datasource; queries auto-use BI Engine if eligible.
- Tune: Set cache TTL; monitor in Reservations dashboard.
- Scale: Use orchestration (e.g., Cloud Workflows) to resize dynamically.
Cost Reduction Table:
| Config | Memory Alloc | Monthly Queries | Without BI Engine | With BI Engine | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Team | 16 GiB | 100 (1 TiB total) | $6.25 | $0.40 | 94% |
| Enterprise | 128 GiB | 1,000 (10 TiB) | $62.50 | $4.00 | 94% |
BigQuery SQL optimization (high cost from syncs).
High sync costs from full-table reloads/scans (e.g., dbt/Airbyte syncs scanning 10 TiB = $62.50/month). Optimize with incremental SQL (MERGE new data), partitioning, and materialized views. Practically, refactor a daily sync from $50 to $5 by appending only changes.
Steps:
- Identify: Query JOBS for sync jobs >100 GiB.
- Incremental SQL: Use MERGE for upserts: MERGE target t USING source s ON t.id = s.id WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE … WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT ….
- Partition: PARTITION BY DATE(sync_date).
- Tools: dbt incremental models; Airbyte append mode.
- Test: Dry-run before prod; monitor post-sync scans.
Optimization Examples Table:
| Sync Type | Original SQL (High Cost) | Optimized SQL | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Reload | CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE target AS SELECT * FROM source; (10 TiB scan) | MERGE target AS t USING (SELECT * FROM source WHERE date > LAST_SYNC) s … (0.1 TiB) | 99% |
| Daily Append | INSERT INTO target SELECT * FROM source; (full scan if unpartitioned) | Partitioned + WHERE date = CURRENT_DATE() | 90% |
Other Calculators :
- Solar Calculator India
- Energy Saving Cost Calculator
- Boolean Algebra Calculator
- Geothermal Cost Calculator
- Old Phone/Mobile Cost Calculator
- BigQuery Cost Calculator
- Solar Pump Cost Calculator
- Author bio: “Updated Jan 2026 by finance/tech experts at CalculateOnline.org”.
- Sources: Link to official Google Cloud Pricing prominently.
- Disclaimer: “Always verify on official Google Cloud Pricing page—rates can change (e.g., multi-region GCS transfer fees starting Feb 2026)”.
FAQs
Can I calculate Bigquery Cost based on table size?
Yes
How to estimate Bigquery Cost before running Query?
You can estimate the cost by checking how many bytes your query will process
Is there any tool to Calculate Bigquery Cost Free
Does the BigQuery calculator work for both flat-rate and on-demand pricing?
Yes
What factors affect BigQuery cost and how to reduce it?
Query complexity, table size, use of partitions or clustering, and frequency all impact cost. To reduce cost, use partitioned tables, avoid SELECT *, and filter rows as much as possible.
Bigquery Cost per TB ?
Cost of Bigquery per TB is 4.88$ or ₹450-480
Bigquery Cost per GB
BigQuery’s on-demand query cost is approximately $0.0061 per GB scanned ($6.25/TiB, free first 1 TiB/month), while active storage is ~$0.023/GB/month and long-term ~$0.016/GB/month (free first 10 GiB/month
How much does it cost to run 100gb query in bigquery ?
Running a 100 GB query in BigQuery (on-demand pricing) scans approximately 0.0977 TiB of data, costing about $0.61 at the standard rate of $6.25 per TiB. However, the first 1 TiB of queries per month is free, so this falls under the free tier and costs $0.
For capacity pricing, it depends on your slot reservations (e.g., Standard Edition: ~$0.04/slot-hour), but queries are unlimited within slots. Use the BigQuery pricing calculator for exact estimates.
